SOA
platform architecture
IBM
Cognos BI delivers a broad range of business intelligence capabilities on an
open, enterprise-class platform. All capabilities—including viewing, creating and
administering dashboards, reports, analysis, scorecards, and events—are
accessed through web interfaces.
The
IBM Cognos Platform delivers the qualifications to manage business intelligence
functions with centralized, web-based administration that provides a complete
view of system activity as well as system metrics and thresholds so that
organizations can resolve potential issues before there is a business impact.
The IBM Cognos Platform is built on a web-based service-oriented-architecture
(SOA) that is designed for scalability, availability, and openness. This
n-tiered architecture is consists of three server tiers:
- The
web tier
- The
application tier
- The
data tier
These server tiers are based up on the business function and can be separated by network firewalls. Reliability
and scalability were key deliberations when designing the IBM Cognos Platform.
Services in the application tier operate on a peer-to-peer basis, which means
that no service is more important and that there are loose service linkages.
Any service of the same type, on any machine in an IBM Cognos Platform
configuration, can satisfy an incoming request, which results in complete fault
tolerance. The routing of requests is done in an optimal way, with automatic
load complementary built into the system.
The
IBM Cognos Platform provides optimized access to all data sources, including
relational data sources and online analytical processing (OLAP), with a single
query service. In addition, this query service understands and takes benefit of
the data source strength by using a grouping of open standards such as SQL99,
native SQL, and native MDX to optimize data retrieval for all these different
data providers. The IBM Cognos BI user interfaces are accessed through the web
tier.
IBM
Cognos Platform server roles
To
ensure optimal performance, IBM Cognos Platform services are normally grouped
together to fulfil certain roles inside a distributed deployment for business
intelligence applications. These server roles also classify the tier within the
architecture that an IBM Cognos BI server uses.
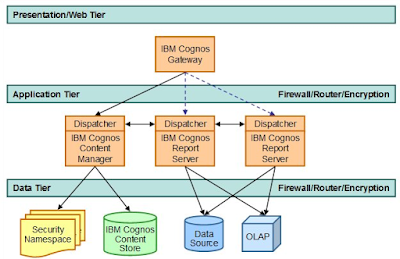
Web
tier: The IBM Cognos Gateway
The
web tier provides user session connectivity to IBM Cognos BI applications. The
IBM Cognos components that fulfil this role are referred to as the IBM Cognos
Gateway.
The
IBM Cognos Gateway component manages all web communication for the IBM Cognos Platform.
The workload on the IBM Cognos Gateway server requires minimal processing
resources. For high availability or scalability Data Source OLAP IBM Cognos
Content Store Security Namespace Security Namespace IBM Cognos Gateway
Dispatcher IBM Cognos Report Server Dispatcher IBM Cognos Report Server
Dispatcher IBM Cognos Content Manager Data Tier Firewall/Router/Encryption
Application Tier Firewall/Router/Encryption Presentation/Web Tier 12 IBM Cognos
Business Intelligence , you can deploy multiple redundant gateways along
with an external HTTP load-balancing router.
Application
tier: Server components
The
application tier for the IBM Cognos Platform is made up of three main server
components:
- IBM
Cognos Dispatcher
- IBM
Cognos Report Server
- IBM
Cognos Content Manager
Application
tier servers are tranquil of a collection of loosely-coupled Java™ and C++
services.
IBM
Cognos Dispatcher
IBM
Cognos Dispatcher performs the load balancing of requests at the application
tier. The IBM Cognos Dispatcher component is a lightweight Java servlet that
manages (and provides communication between) application services. At startup,
each IBM Cognos Dispatcher registers locally available services with the IBM
Cognos Content Manager. During the normal operation of IBM Cognos BI services,
requests are load balanced across all available services using a configurable,
weighted round-robin algorithm to distribute requests. You can adjust the
performance of IBM Cognos Platform by defining how IBM Cognos Dispatcher handles
requests and manages services.
Threads
within IBM Cognos Platform are managed by the type of traffic that they handle,
which is referred to as high and low affinity. Affinity relates to the report
service process that handled the original user request when multiple
interactions need to occur to satisfy the request. High-affinity connections
are used to process total and high-affinity requests from the report services.
Low-affinity connections are used to process low-affinity requests. A high affinity
request is a transaction that can gain a performance benefit from a previously
processed request by accessing cache. It can be processed on any service, but
resource consumption is minimized if the request is routed back to the report
service process that was used to execute the original process. A low affinity
request operates just as professionally on any service.
IBM
Cognos configuration: A normal configuration for IBM Cognos Dispatcher is two IBM
Cognos Report Server processes allocated processor and eight to 10 threads per
processor in one of the following configurations:
- Three
low affinity threads plus one high affinity thread
- Four
low affinity threads plus one high affinity thread
We
can manage the number of threads per IBM Cognos BI reporting service process
through the IBM Cognos Platform administration relieve by setting the number of
high- and low-affinity connections
IBM
Cognos Report Server
The
main service that is responsible for application-tier processing is the report
or query service .IBM Cognos Dispatcher starts IBM Cognos Report Server
processes animatedly as needed to handle the request load. An administrator can
identify the maximum number of processes that these services can start, as well
as the minimum number of processes that should be running at non-peak times.
arrange the number of processes for IBM Cognos Report Server based on the
available processor capacity.
In
general, IBM Cognos BI reporting service performance is closely tied to
processor clock speed and throughput capabilities. The number of processors in
a server and their clock rates are the two primary factors to consider when
planning for additional IBM Cognos Report Server hardware capacity. For
example, you generally configure a server with four available processors to use
more report service processes than a server with only two available processors.
Similarly, given two servers with an equal number of processors, configure the
server with a considerably faster processor clock rate to have more report and
report-service processes.
When
configuring the IBM Cognos Platform server environment, you must set a Java
heap size. The IBM Cognos BI reporting and query service is made up of two
underlying components:
- The
Java servlet-based IBM Cognos Dispatcher services
- Report
services that are launched using the Java Native Interface (JNI)
Set the Java virtual machine (JVM) heap-size allocation for IBM Cognos Platform
so that Java memory is only as large as is necessary to accommodate the
processing requirements of the Java based services. This setting ensures that
as much memory as probable is available to the IBM Cognos Report Service, which
is not Java. You can decide the optimal Java heap size using Java garbage
collection statistics.






Nice post .Keep updating Cognos TM1 online training hyderabad
ReplyDeleteThis post is very intresting and useful one for us.Keep updating more blog posts.
ReplyDeleteThank you...
cognos tm1 training